USD/CAD Price Forecast: Hangs near multi-month low; seems vulnerable around 1.3800
- USD/CAD meets with a fresh supply on Tuesday amid sustained USD selling bias.
- Subdued Crude Oil prices and domestic political uncertainty might cap the CAD.
- The technical setup favors bears and supports prospects for further depreciation.
The USD/CAD pair struggles to capitalize on the overnight bounce from the 1.3780 region, or a six-month low, and attracts fresh sellers during the Asian session on Tuesday. Spot prices drop to the 1.3800 mark in the last hour and seem vulnerable to slide further amid a broadly weaker US Dollar (USD).
US President Donald Trump’s back-and-forth tariff announcements have weakened investors' confidence in the US economic growth and dented the USD's safe-haven appeal. Adding to this Trump's attack on Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell raised doubts about the central bank’s independence and keeps the USD depressed near its lowest level since April 2022 touched on Monday. This, in turn, is seen as a key factor exerting downward pressure on the USD/CAD pair.
Meanwhile, Crude Oil prices struggle to attract any meaningful buyers and remain below a two-week high touched on Friday amid worries that an all-out trade war would push the global economy into recession and dent fuel demand. This, along with domestic political uncertainty ahead of the Canadian snap election on April 28, could undermine the commodity-linked Loonie and lend support to the USD/CAD pair, though any meaningful bounce still seems elusive.
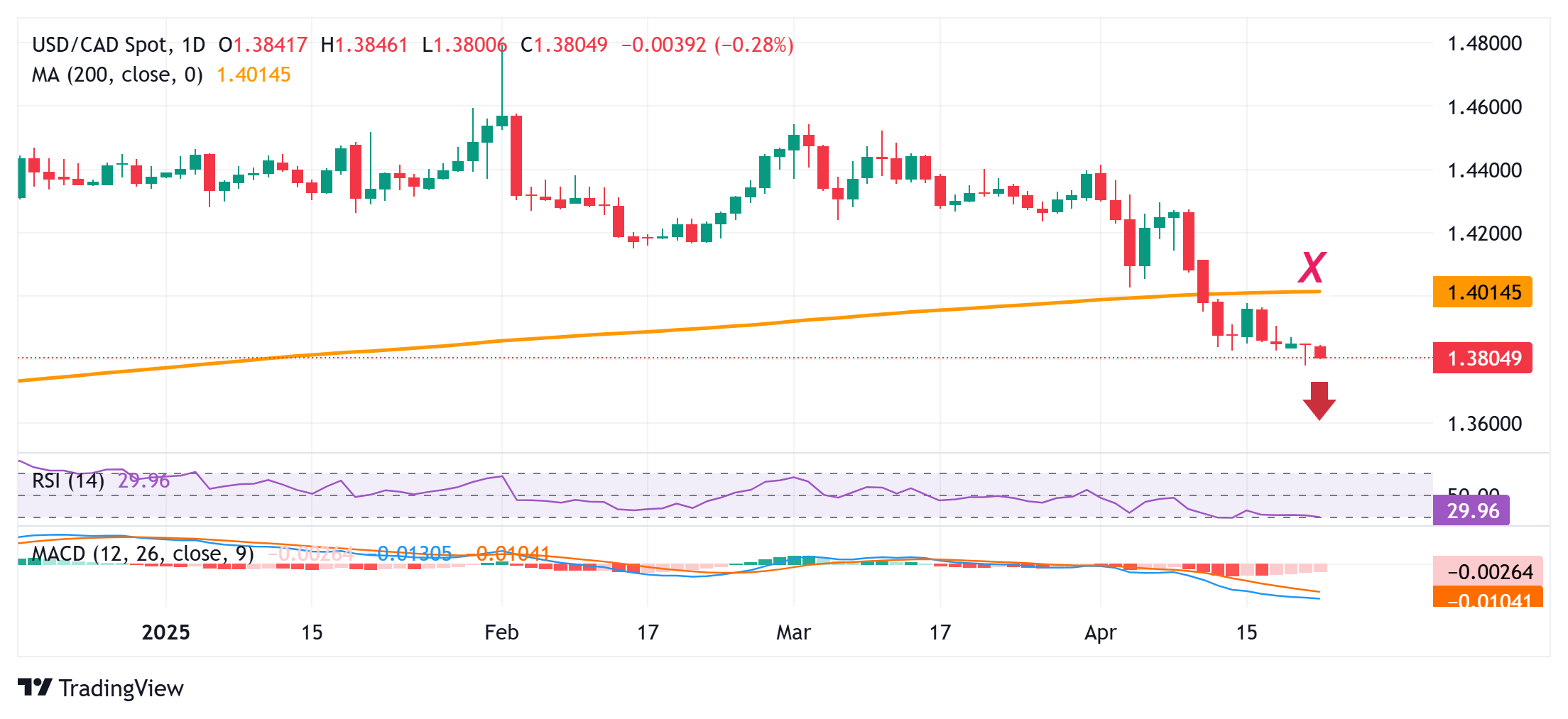
From a technical perspective, the recent breakdown below the very important 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA), for the first time since October 2024, was seen as a fresh trigger for bearish traders. Moreover, oscillators on the daily chart are holding deep in negative territory, suggesting that the path of least resistance for the USD/CAD pair remains to the downside. Hence, an attempted recovery is more likely to get sold into and remain capped near mid-1.3800s.
Some follow-through buying, however, could trigger a short-covering rally and allow spot prices to reclaim the 1.3900 round figure. The momentum could extend further towards the 1.3950-1.3955 intermediate hurdle en route to the 1.3975-1.3980 supply zone, though it runs the risk of fizzling out near the 1.4000 psychological mark or the 200-day SMA.
On the flip side, weakness below the multi-month low, around the 1.3780 region touched on Monday, will reaffirm the negative bias and pave the way for further losses. The USD/CAD pair might then slide further towards the 1.3750-1.3745 support before eventually dropping to the 1.3700 mark and the next relevant support near the mid-1.3600s.
USD/CAD daily chart
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.


