US President Trump clarifies 20% tariffs on Chinese imports of semiconductors, electronics
Late Sunday, US President Donald Trump took to his own social media application, Truth Social, and clarified that there will be no tariff exemption on semiconductors and the electronics supply chain, as these products will be subject to the existing 20% tariffs on fentanyl and not the 145% hike.
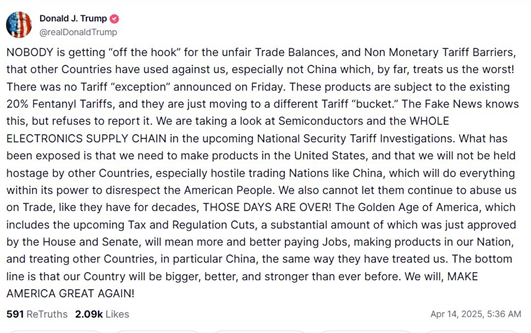
This comes after the US Customs and Border Protection issued a guidance late Friday stating certain items like smartphones, laptops, hard drives, flat-panel monitors, semiconductors etc would be exempted from both Trump’s 10% baseline reciprocal tariffs and the 145% tariffs on Chinese imports.
However, US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick said in an ABC News interview on Sunday that smartphones, computers and some other electronics, just exempted from steep tariffs on imports from China, would face separate new levies along with semiconductors within the next two months.
Lutnick added that he is “not concerned about the US Dollar. “
Meanwhile, US Trade Representative (USTR) Jamieson Greer told CBS News on Sunday that President Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping "don't have any plans" to speak amid an escalating trade war between the two countries.
“We have to be much more deliberate about the semiconductor supply chain,” he said on the latest tariff talks on electronics and semiconductors.
Market reaction
Amid news of not-so-steep tariffs on Chinese imports of the electronic supply chain, risk sentiment is in a sweeter spot at the start of the new week early Monday, with the US Dollar Index holding the tepid recovery from three-year lows.
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.


